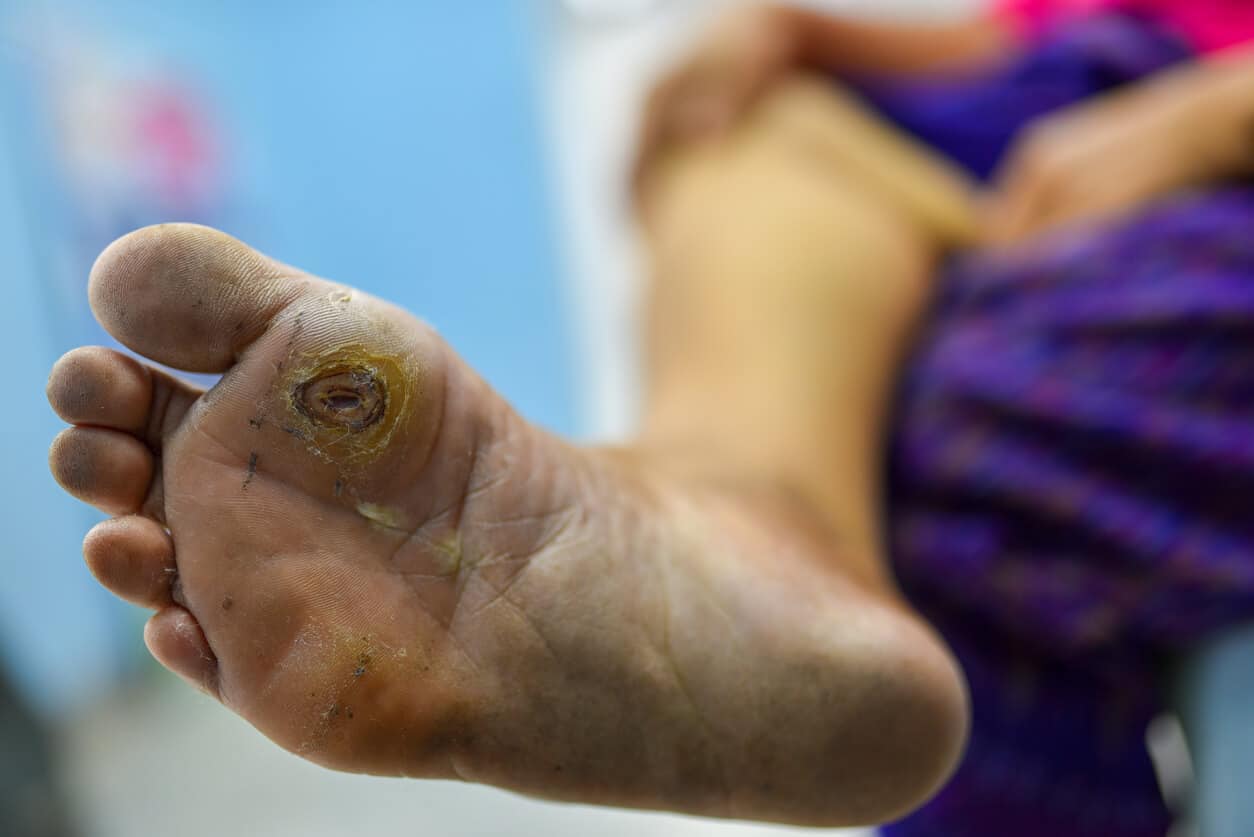
Diabetic gangrene is a serious complication that arises from uncontrolled diabetes, often resulting from poor blood circulation, nerve damage, and persistent infection. Patients with diabetes are at higher risk of developing tissue necrosis, particularly in the lower extremities, which can progress rapidly if not managed properly. Dry gangrene, which typically develops gradually, is often painless but still requires urgent care. Wet gangrene, on the other hand, is associated with infection and swelling, and it can spread quickly, posing life-threatening risks. Recognizing early symptoms such as discoloration, foul odor, or persistent ulcers can significantly influence treatment outcomes. Orthopedic care plays a crucial role in managing these conditions, aiming to preserve limb function, prevent infections from worsening, and improve patients’ overall quality of life. Understanding the mechanisms of diabetic gangrene is essential for patients, caregivers, and healthcare providers to make timely decisions.
Orthopedic specialists are integral to the management of diabetic gangrene because they focus not only on repairing or removing damaged tissue but also on maintaining the patient’s mobility and preventing further complications. Coordination between orthopedic surgeons, endocrinologists, and vascular specialists ensures a comprehensive treatment plan tailored to each patient. The primary objectives of orthopedic treatment include controlling infection, preserving as much of the limb as possible, and preventing recurrence. Orthopedic care often involves both surgical and non-surgical interventions, depending on the severity of tissue damage and the patient’s overall health. By addressing musculoskeletal and vascular issues simultaneously, orthopedic treatment significantly reduces the risk of major amputations. Moreover, patients benefit from personalized care plans that consider lifestyle factors such as blood sugar management and activity level. The expertise of orthopedic teams in wound care and surgical interventions can drastically improve recovery timelines.
Accurate diagnosis is a cornerstone of effective orthopedic treatment for diabetic gangrene. Imaging techniques like X-rays, MRI, and CT scans allow physicians to determine the extent of bone and tissue involvement, which guides the choice of treatment. Laboratory tests help monitor infections and identify specific bacterial strains, ensuring that antibiotic therapy is targeted and effective. Evaluating comorbid conditions such as heart disease or kidney dysfunction is essential, as these can affect healing and surgical outcomes. Orthopedic assessments also focus on the degree of necrosis and the potential for limb salvage, helping clinicians make informed decisions. Regular monitoring allows early intervention when complications arise, preventing minor issues from escalating into severe problems. By combining diagnostic tools with clinical expertise, orthopedic teams can create treatment strategies that are precise, efficient, and patient-centered.
Non-surgical orthopedic approaches play a significant role in managing diabetic gangrene, particularly in the early stages. Wound care management, including debridement of dead tissue, reduces bacterial load and promotes healing. Specialized orthopedic footwear and offloading devices help redistribute pressure on the feet, preventing ulcers from worsening. Hyperbaric oxygen therapy may be used to enhance tissue oxygenation, which can accelerate healing and decrease the risk of infection. Antibiotic therapy is often prescribed based on laboratory results, targeting specific pathogens to prevent systemic infection. Non-surgical interventions are also essential for maintaining mobility while the affected limb heals. Patient adherence to these treatments, combined with regular follow-ups, often determines the overall success of non-invasive management strategies.
In cases where tissue damage is extensive or infection threatens systemic health, surgical orthopedic interventions become necessary. Procedures may range from minor amputations of toes or parts of the foot to more complex limb salvage operations. Revascularization surgeries restore blood flow to affected areas, supporting tissue recovery and reducing gangrene progression. Post-operative rehabilitation is critical, helping patients regain mobility and adapt to any functional limitations. Surgical approaches are often paired with intensive infection control, including intravenous antibiotics and close monitoring of wound healing. Surgeons aim to minimize tissue loss while addressing the underlying causes of gangrene, such as poor circulation or pressure-related injuries. Long-term follow-up ensures that complications are detected early and managed appropriately, further improving patient outcomes.
Multidisciplinary care enhances the effectiveness of orthopedic treatment for diabetic gangrene. Collaboration among endocrinologists, vascular surgeons, podiatrists, and orthopedic specialists ensures comprehensive management of both diabetes and its complications. Patients benefit from lifestyle guidance, including diet modifications, regular blood sugar monitoring, and smoking cessation, all of which support tissue healing. Foot care education, proper hygiene, and early recognition of warning signs help prevent recurrent gangrene. Orthopedic teams often coordinate with rehabilitation specialists to design exercise and mobility programs that protect healing tissues. Patient engagement in their care plan is essential, as adherence to preventive measures can significantly reduce the risk of further complications. Regular check-ups with orthopedic providers reinforce education and provide timely intervention when necessary.
Advancements in orthopedic treatment for diabetic gangrene are improving outcomes and reducing the risk of major amputations. Emerging technologies, including bioengineered tissues and regenerative medicine, offer new possibilities for tissue repair. Minimally invasive surgical techniques allow for precise removal of necrotic tissue with less trauma, speeding up recovery. Innovations in wound care products, such as antimicrobial dressings and negative-pressure wound therapy, help control infections and promote healing. Orthopedic research continues to explore methods that improve circulation, enhance tissue regeneration, and optimize post-operative recovery. These advances, combined with personalized care plans, empower patients to maintain mobility and reduce the long-term impact of diabetic complications. Staying informed about the latest treatment options is beneficial for both patients and healthcare providers.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
Can diabetic gangrene be completely reversed with orthopedic treatment?
Orthopedic treatment can significantly improve outcomes by preventing further tissue loss and controlling infection, but complete reversal depends on the severity of the gangrene. Early detection and prompt care increase the chances of preserving affected limbs.
How does orthopedic care prevent amputations in diabetic patients?
Orthopedic care focuses on wound management, infection control, and restoring blood flow, which reduces tissue death. Surgical and non-surgical interventions aim to salvage as much of the limb as possible while maintaining mobility.
What is the recovery time after orthopedic surgery for gangrene?
Recovery varies based on the procedure and the patient’s overall health. Minor surgeries may require a few weeks of healing, while complex limb salvage operations may take several months and involve ongoing rehabilitation.
Are there home care techniques recommended by orthopedic specialists?
Yes. Proper foot hygiene, regular inspection of the feet, wearing orthopedic footwear, and adhering to prescribed medications are all crucial. Patients are often advised to monitor blood sugar levels closely to support healing.
How often should diabetic patients at risk of gangrene see an orthopedic doctor?
Patients with high risk should have regular check-ups, often every few months or as advised by their physician. Frequent monitoring helps detect early signs of gangrene and enables timely intervention.
Orthopedic treatment for diabetic gangrene is essential for protecting limbs, preventing infections, and improving the overall quality of life for patients. By combining accurate diagnosis, non-surgical management, surgical intervention when necessary, and multidisciplinary care, orthopedic specialists play a vital role in the fight against diabetic complications. Advances in medical technology continue to offer hope for better outcomes, emphasizing the importance of early detection, consistent care, and patient education.