Understanding Diabetic Foot Disease
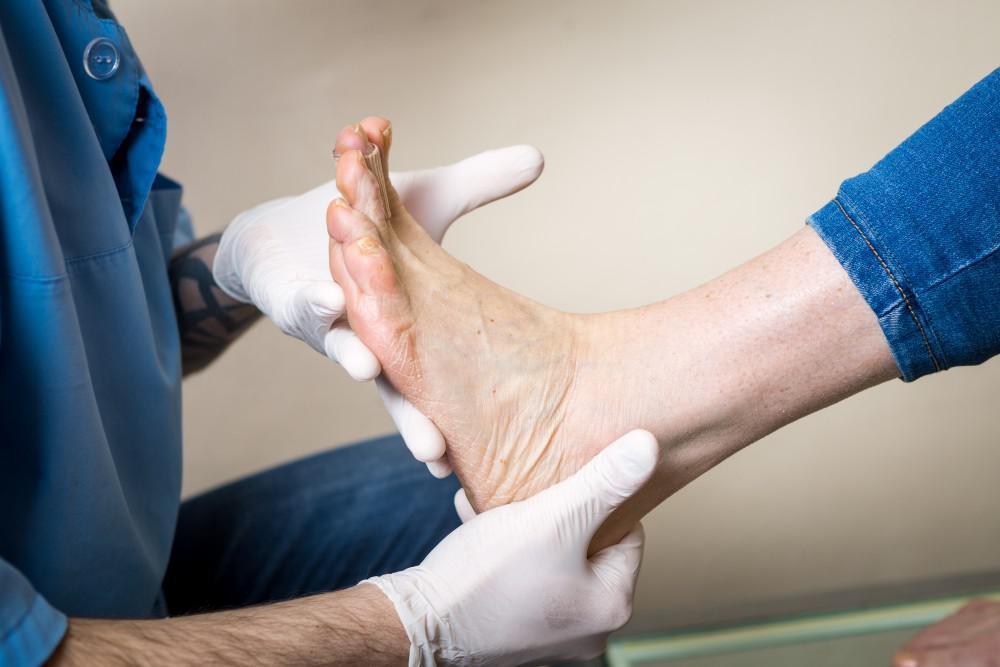
Diabetic foot disease is one of the most challenging complications that people with diabetes face, primarily because it affects both mobility and overall quality of life. When blood sugar levels remain high over time, the nerves in the feet can become damaged, leading to a condition known as diabetic neuropathy. This nerve damage often causes loss of sensation, meaning small injuries may go unnoticed until they worsen. Poor circulation, another common problem in diabetes, further reduces the ability of the body to heal wounds effectively. Together, these issues create the perfect environment for infections, ulcers, and orthopedic complications to develop. Orthopedic treatment for diabetic foot disease plays a vital role in preventing these problems from escalating and restoring function to the feet. Recognizing the seriousness of this condition early can help patients avoid irreversible damage and long-term disability.
Common Orthopedic Complications in Diabetic Foot Disease
There are several orthopedic complications that arise when diabetic foot disease is left unmanaged, and each carries risks that affect mobility and independence. One of the most common is foot ulcers, which develop when pressure points or minor injuries break the skin and fail to heal properly. These ulcers can deepen over time, sometimes exposing bone and leading to dangerous infections such as osteomyelitis. Another complication is Charcot foot, where weakened bones and joints in the foot collapse, causing significant deformity and instability. Patients may also experience limited joint mobility due to stiffness, making walking painful and difficult. Orthopedic specialists often see how quickly minor wounds can progress to severe infections when circulation and nerve function are compromised. In advanced cases, untreated conditions can lead to amputation, which underscores the importance of timely orthopedic treatment. By understanding these complications, patients and caregivers can better appreciate why specialized orthopedic care is necessary.
The Role of Orthopedic Specialists in Managing Diabetic Foot Disease
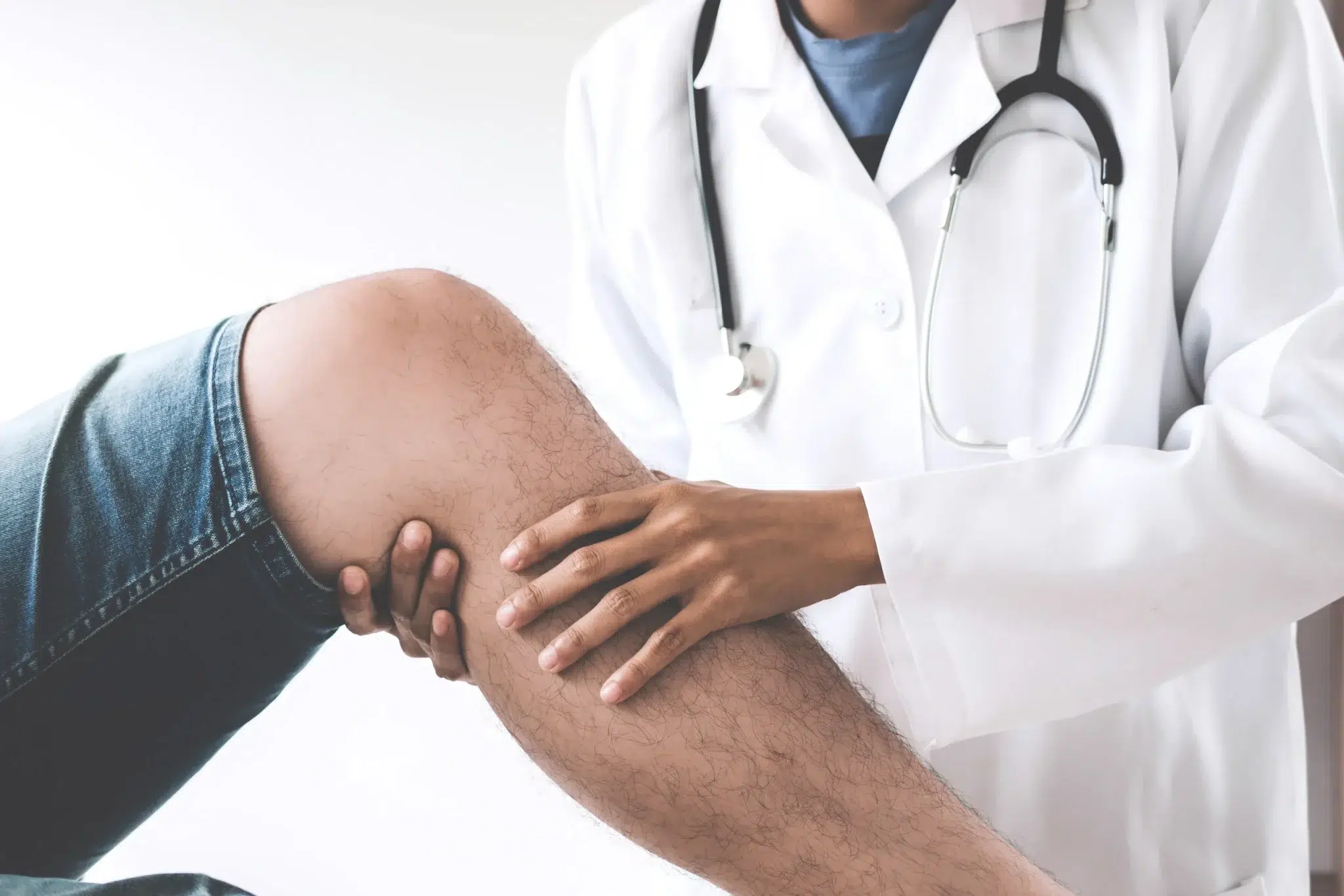
Orthopedic specialists are central to the care of patients with diabetic foot disease because they address the structural, mechanical, and healing aspects of the condition. They often work alongside endocrinologists, podiatrists, vascular surgeons, and wound-care nurses to create a multidisciplinary plan tailored to each patient. A key part of their role is assessing deformities or structural changes in the foot that may lead to further injury. Diagnostic tools such as X-rays, MRIs, and vascular studies are frequently used to evaluate bone health, blood flow, and soft tissue conditions. This careful evaluation helps specialists determine whether conservative or surgical approaches are most appropriate. Orthopedic treatment for diabetic foot disease is not only about addressing current problems but also about preventing future complications. Patients who regularly consult with orthopedic specialists tend to maintain better mobility and reduce their risk of serious foot damage.
Non-Surgical Orthopedic Treatment Approaches
Not all patients with diabetic foot disease require surgery, and many benefit from non-invasive orthopedic treatments that support healing and mobility. Orthopedic footwear, custom insoles, and braces are designed to provide proper alignment, reduce pressure points, and protect vulnerable areas of the foot. Offloading devices, such as specialized boots or casts, are often used to relieve pressure from ulcers, allowing them to heal without constant strain. Wound care is also closely tied to orthopedic management, as proper footwear and pressure relief prevent wounds from reopening or worsening. Physical therapy can help restore strength, flexibility, and balance, improving overall stability and independence. Lifestyle changes, such as weight management and regular exercise under orthopedic guidance, further enhance outcomes. Through consistent monitoring and adjustments, orthopedic specialists can help patients manage diabetic foot disease without resorting to surgery. These methods highlight the importance of early orthopedic involvement in care.
Surgical Orthopedic Interventions
When non-surgical methods are not enough, orthopedic surgery becomes an essential option for patients with advanced diabetic foot disease. Surgery may be required to correct deformities caused by Charcot foot, where bones collapse and cause severe structural problems. In some cases, infected tissue must be removed through debridement to stop infections from spreading deeper into the body. Surgical drainage may also be necessary if abscesses form around the foot or ankle. Tendon lengthening and realignment procedures are another approach, as they can redistribute pressure across the foot and reduce the risk of recurring ulcers. For patients with widespread damage that cannot be repaired, amputation may be the last resort, followed by rehabilitation and prosthetic support to restore mobility. While the thought of surgery may be intimidating, advancements in orthopedic procedures have improved recovery times and outcomes for diabetic patients. Orthopedic treatment for diabetic foot disease ensures that surgical interventions are carefully chosen and performed with the patient’s long-term mobility in mind.
Innovations in Orthopedic Treatment for Diabetic Foot Disease
Orthopedic care has advanced significantly in recent years, offering diabetic patients more options for healing and recovery. One area of innovation is advanced wound-healing techniques, including bioengineered skin substitutes and growth factor therapies, which work alongside orthopedic support to speed recovery. Minimally invasive surgeries are also becoming more common, reducing recovery time and lowering the risk of complications. Regenerative medicine, such as stem cell therapy, is being studied for its potential to repair damaged tissues and improve blood flow in the feet. Another exciting development is the use of 3D printing in creating customized orthopedic footwear and implants tailored to a patient’s exact needs. These technologies offer hope for patients who might have previously faced limited treatment choices. Orthopedic specialists are at the forefront of adopting these innovations to improve patient outcomes. As research continues, diabetic patients can expect even more advanced options in managing foot disease.
Preventive Orthopedic Strategies for Patients with Diabetes
Prevention remains the best strategy for diabetic foot disease, and orthopedic care plays a major role in keeping patients safe. Daily foot checks are recommended so that patients can detect small cuts, blisters, or signs of infection before they progress. Orthopedic assessments help identify risk factors such as poor footwear, bone deformities, or improper weight distribution. Patients are often advised to wear shoes designed specifically for diabetic feet, as these reduce the chances of pressure-related ulcers. Exercise is encouraged but should be guided by orthopedic professionals to ensure that activities do not place unnecessary strain on vulnerable areas. Nutrition also supports orthopedic health, with a balanced diet contributing to stronger bones and better circulation. Regular follow-ups with orthopedic specialists allow for early adjustments to treatment plans as the patient’s condition changes. By adopting these preventive strategies, patients can significantly reduce their risk of developing severe diabetic foot complications.
Living Well with Orthopedic Support for Diabetic Foot Disease
Orthopedic treatment not only addresses the medical challenges of diabetic foot disease but also enhances overall quality of life. With proper support, patients can maintain independence, continue daily activities, and avoid the fear of losing mobility. Education is a key part of living well, as orthopedic specialists teach patients how to care for their feet and recognize warning signs. Emotional and psychological well-being is also important, as diabetic foot disease can sometimes lead to stress or depression. Rehabilitation programs often include counseling, group support, and adaptive strategies to help patients feel empowered. Orthopedic care ensures that patients are not defined by their condition but can instead focus on living active and fulfilling lives. With the right guidance, diabetic patients can overcome many of the challenges associated with foot disease.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
1. What is the role of an orthopedic doctor in treating diabetic foot disease?
Orthopedic doctors specialize in treating the bones, joints, and structural issues that affect the feet. In diabetic foot disease, they evaluate deformities, provide supportive devices, and perform surgeries when necessary to restore function.
2. How do orthopedic shoes help manage diabetic foot problems?
Orthopedic shoes are designed to reduce pressure points, improve alignment, and protect against injuries that could lead to ulcers. They play a critical role in prevention and long-term foot health.
3. When should a patient consider orthopedic surgery for diabetic foot complications?
Surgery is usually considered when conservative treatments fail, or when infections, deformities, or severe pain threaten mobility or overall health.
4. Can orthopedic treatment prevent amputation in diabetic patients?
Yes, timely orthopedic treatment can prevent many cases of amputation by addressing ulcers, infections, and structural problems before they reach an advanced stage.
5. What are the latest advancements in orthopedic care for diabetic foot disease?
Advancements include minimally invasive surgeries, regenerative medicine, stem cell therapy, and 3D-printed orthopedic devices that provide personalized solutions for patients.